Property Price Estimation using Webscrapping and Machine Learning with Heroku deployment.
Index of this post
- Motivation
- Methodology followed
- Data Collection Strategy
- Handling bad data
- Handling missing data
- Statistical Techniques
- EDA
- Modelling
- Deployment
- Model Retraining Strategy
- Conclusion
Motivation to do this project
I had pursued a 6 month internship at Sunteck realty ltd. from May to September 2019. There I was in the Sales and marketing team but for a brief part of the internship. Work done at Sunteck realty involved:
- Competition Analysis.
- Market Analysis of brand preferences of people at Naigaon.
- Explaining about the property to potential clients by phone and across the table for various projects of Sunteck.
- Metting channel partners to understand the market and invite them to the project so that they could generate business for Sunteck.
- Part of organising events at Signia Waterfront Airoli to create more awareness for the project. Events were held for social media influencers and for direct clients as well.
An esential part of real estate is to know the sale price of competitors and what are their strengths and weaknesses. While doing competition analysis, the company was highly interested in knowing the pricing of competitors in the market. While during the intership we had to manually visit each site and find out the actual price the property was being sold at, I felt that it would be great to automate this process.
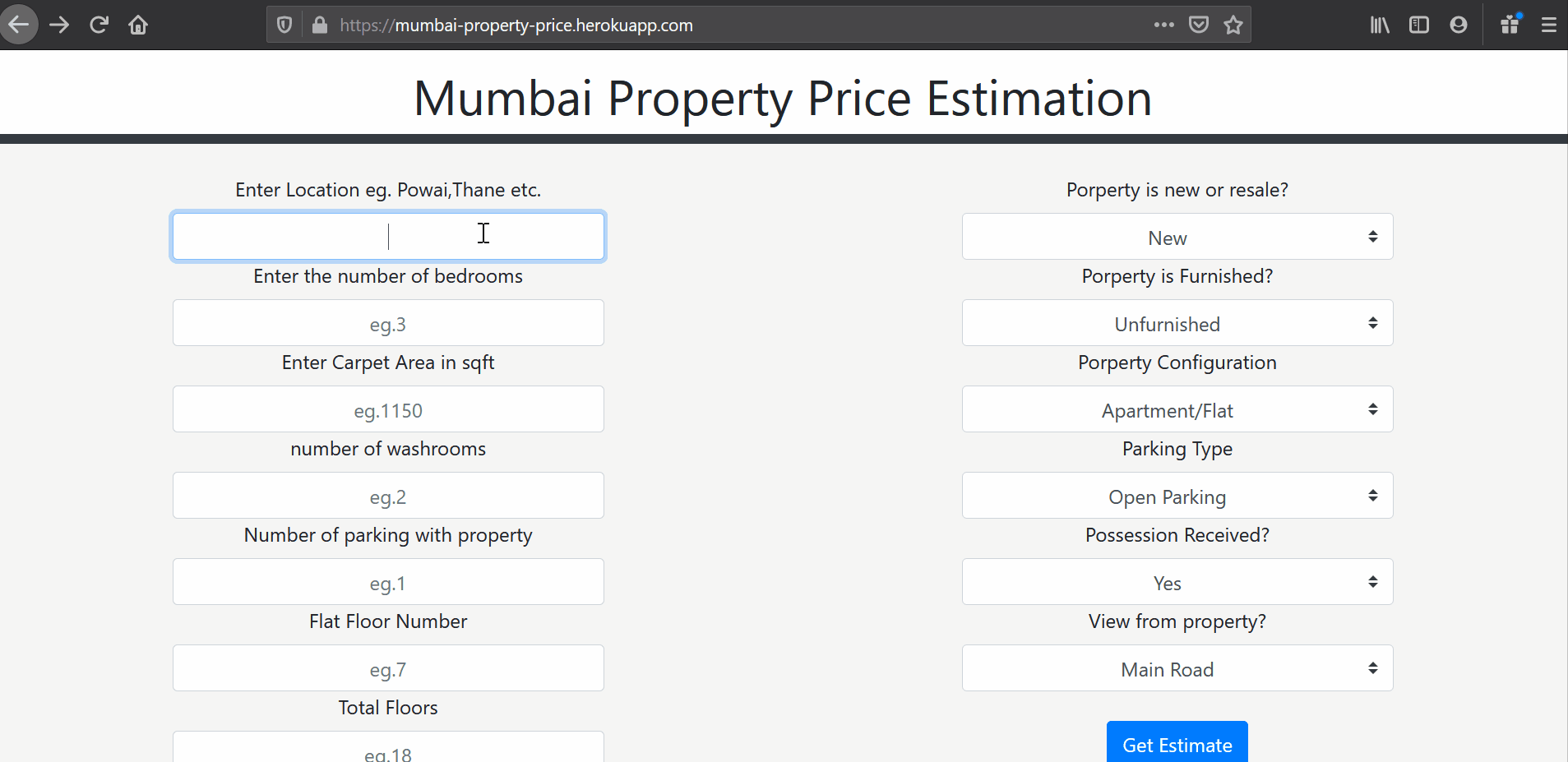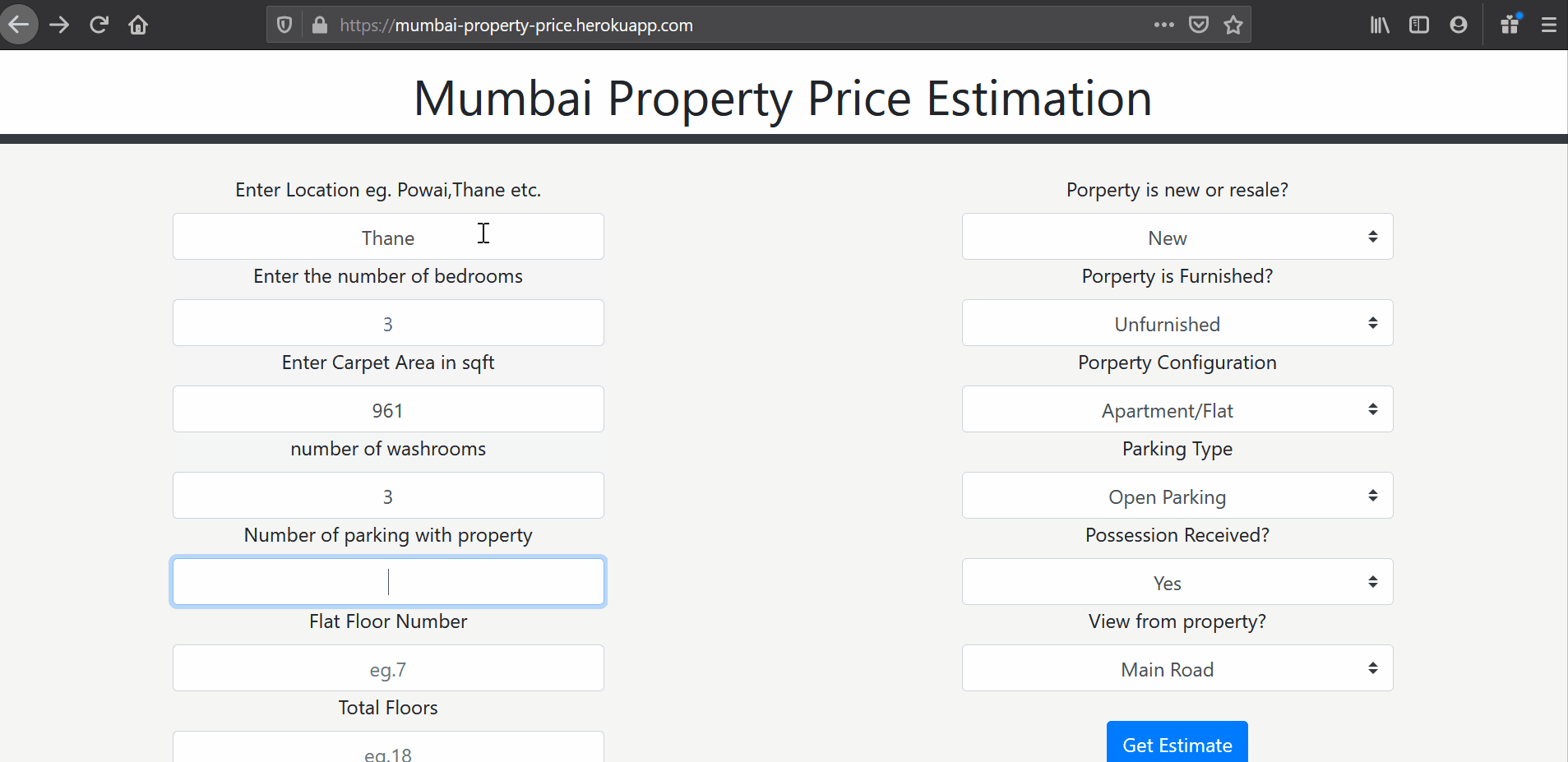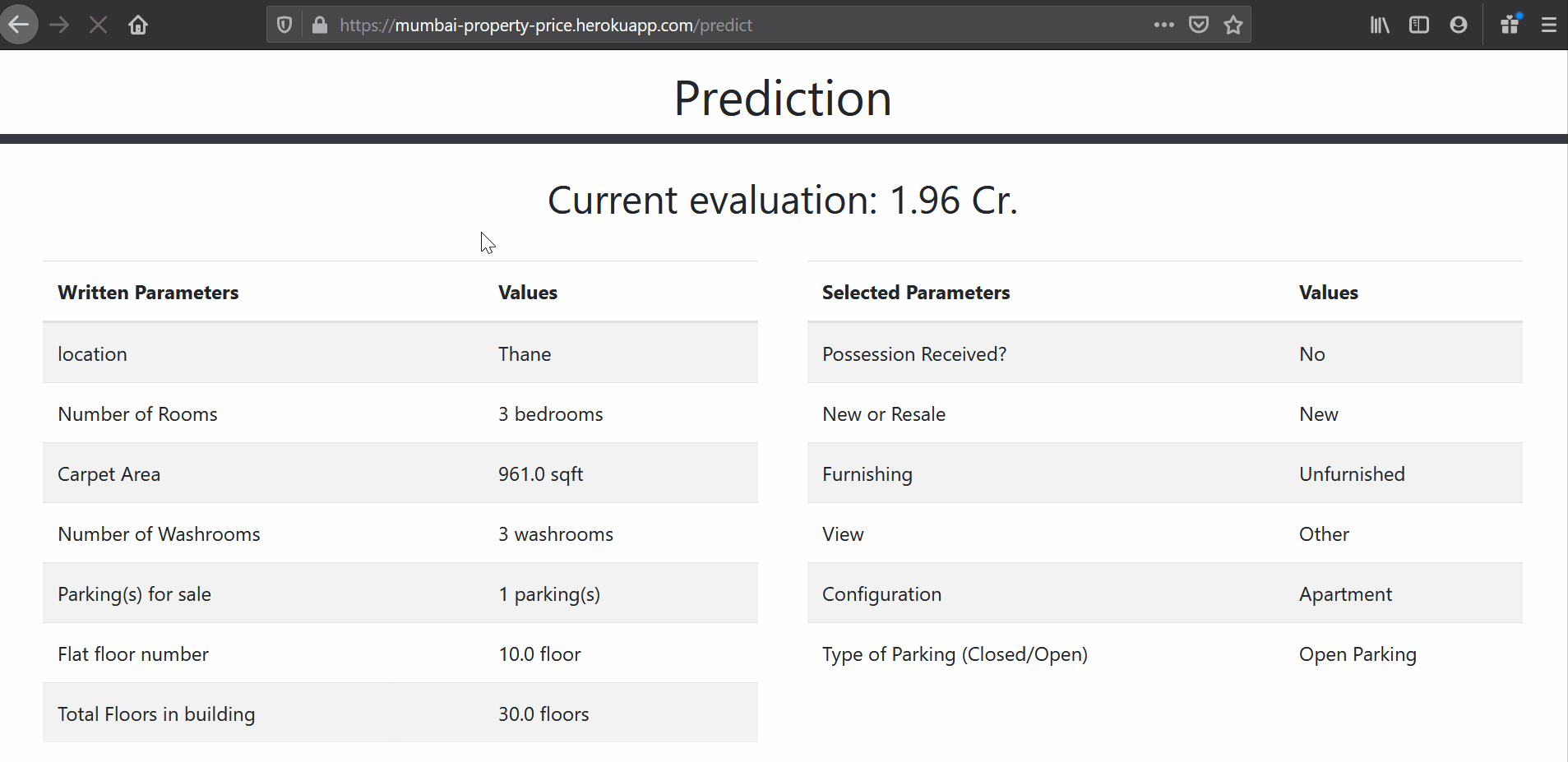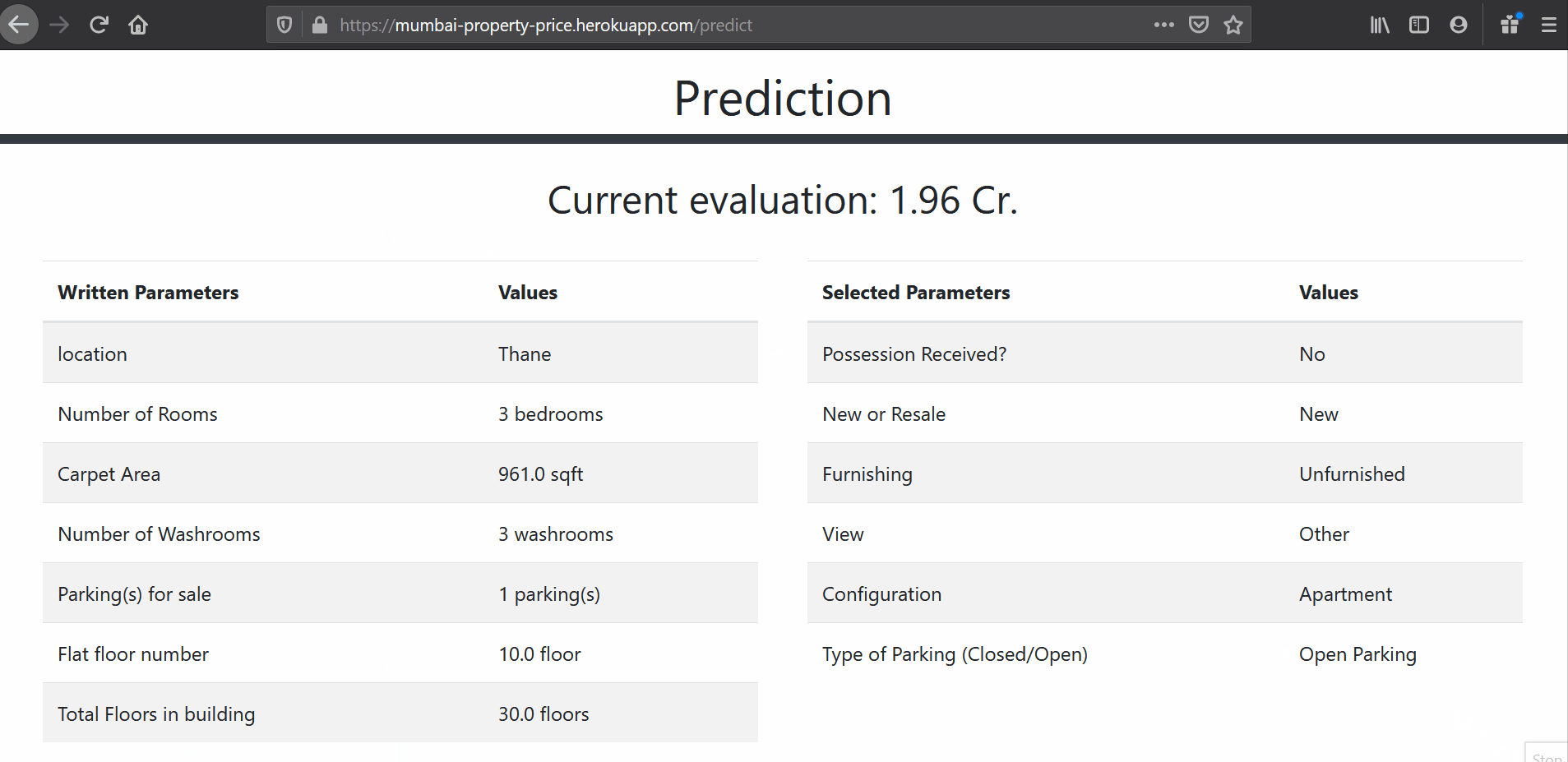
I have developed this “Property Price Estimation” web app for Mumbai based properties for clients as well as builders to know the estimated rates at which a property is going for in their area based on various parameters. This reduces the amount of time spent researching on the internet and visiting various places to find out rates.
Methodology followed
Data Collection Strategy
-
From the website that I was collecting data, they had blocked access to libraries like urllib and url request. The only way to access the website was through a browser. So I decided to use the Selenium python library that would access the website via a browser and I could also code the entire scrapping process in python.
-
Using BeautifulSoup I have passed the output of selenium which is raw html into an html parser. This makes it easier to access each tag in the html which we will use to extract all the relevant data. You can check out the notebook I have written for the scrapping process here.
-
I in no way encourage people to do webscrapping and understand that the hosts server faces the load. Hence I am safely scrapping 40-50 records every 2-3 days to ensure I am not bombarding the hosts system.
Handling Bad Data
Webscrapping issues and challenges:
-
Location:There were records for location that I was collecting as a list of length 2. The 1st was the name of the society and the next was the actual location. Now for some records that were not having a society name mentioned, I was getting “carpet area” or “super area” as the 2nd term. For this I wrote a script that would check for “carpet or super area” as the 2nd term. If yes then the first term would be the location. This works mostly for all records and I have not faced any problems after collecting data across 5 days so I am going to stick to this solution for now.
-
Latitude and Longitude conversion: I was converting the location column to latitude and longitude since the machine only understands numerical data. For this there were locations for which Geopy was not able to indentify the place. For example “JVPD Scheme” or “Vinay Nagar” is not something that is generic enough for Geopy to give me the latitude and longitude. Hence for such records I was creating another csv file called latest_bad_loc.csv where I was saving all these records and was not discarding any of the records.
-
Execution time for scrapping from selenium is acceptable. For extracting 210 records it takes 43 seconds.
-
Extraction of BHK,advertiser and price was easy since it had its own seperate class respectively.
-
Other parameters came under a single class which was a card summary on the page for each property.
-
Finding all classes for each records takes some time in html parser. However converting these records into a numpy array is a better strategy since arrays are faster and occupy lesser memory space.
-
Posted Date was present under another class name so I was not able to use the same function to extract the card parameters that I was using for many of the parameters. I also had to tackle certain records that had yesterday and today instead of the date. Used my own date function to tackle this problem.
-
There were some records that had “for sale” before location and some had “for sale in” before location. Luckily there were only these 2 versions of this value in each card_record. So I had to write a seperate loop for location to check for both “for sale” and “for sale in”.
-
Lastly I wrote code that would concat any new records to the previous csv created so that my database keeps increasing.
-
Since I have written code for concatinating, we can automate this script to run every week or everyday and capture 50-100 records per day to get latest records added into are dataset.
-
Lastly in future I would like to store this information in an S3 bucket on amazon aws or any other cloud based solution that is of least cost.
Handling Missing Data
-
For most of the features I used the standard methods of handling missing data (mean,median and mode). If there were columns that had missing data over 60% I would drop it however the data is still present in the csv file and is just not being used for the modelling process.
-
However if an important column like price or area which usually never gives me null values has some records missing then I would drop such records since it would be a very small percentage of the entire data.
-
Location column that was collected through webscrapping was in the form of a string list. 1st I removed the square brackets and then seperated by , to convert to a list. Then I extracted location and society name and created 2 new columns. Also while scrapping if in the entry there was no mention of society name then for last param of location we are getting carpet area. This could be solved by only considering the 1st value as location for any records having carpet area or super area.
-
Floors had nan values and I was not able to understand how to fill these values. I decided to drop these columns since we will be collecting data everyday and floor information is essential for the price.
-
Parking This column seemed to have many anomalies and also had mentions of open and closed parking. So I created 2 columns, 1 for the number of parking spaces and the other for the type of parking and checked whether either no. of parking or type of parking had any impact on price. I found the number of parking spaces has a higher impact on price than type of parking but only when the number of parking spaces is more than one. There is not much difference in house price when no. of parking is 0 or 1. I used the anova test for the type of parking space and p-value of ttest for number of parking here since I had bucketed parking into 3 categories which were both,covered and open parking. Tukey hsd told me that covered parking seemed to have the most significant impact on price compared to open parking and both.
-
Location conversion to latitude and longitude This column according to my knowledge plays a significant role in the pricing of a property. Installing geppandas gave me some trouble however I was able to solve it by installing the library as administrator. I wanted to save whichever locations I have got since I did not want to call the geopy object again and again for the same location. Latitude can be around 18 or 19 only and longitude around 72 or 73 degrees for Mumbai. Since not everyone puts generic location it becomes difficult to extract latitude and longitude. We are saving such records into a seperate file called bad records and not discarding it. This allows us to check whether such a bad column ever occurs again reducing execution time.
Statistical Techniques
- I used the ttest_ind function from stats library for columns having 2 categories and compared it with price.
- Used Anova test and Tukey HSD to check for difference in mean of price for each category against the other.
Exploratory Data Analysis
- Univariate Analysis:
-
Looking at the distributions of all numerical features I observed that area,total_floors,flat_floor_no and price of property were all skewed. Applying log transformation to these columns reduced the skewness significantly making the data more normally distributed. The same imputations are also done to data entered by users and exponent of prediction is taken since our target is predicted on the log scale.
-
Created normalized count plots for each categorical variable to check how many records are present in each category.
-
-
Bivariate Analysis:
-
Created boxplots to determine how the price or target variable is distributed across each category with each categorical feature. While there were some price outliers within each category, I was not going to drop any values since I was going to take a log transformation anyway. However it is advised to try to get rid of any outlier using maybe the IQR method.
-
Created scatter plots to see relations between all numerical parameters with price. The scatter plots made it certain that there was skewness which we had observed in the univariate analysis.
-
Modelling
-
Linear Regression
- The initial Linear Regression model was giving is a poultry r2_score of 52%.
- After performing the 5 tests of regresison which are linearity, normality, auto-correlation, heteroskedasticity and multicollinearity I was able to get the r2_score up to 73%. The main factor was performing log transform on the target variable that removed any heteroskedasticity present in the model.
-
Next we performed regularization techniques and were able to reduce the test and train r2_score difference to less than 3%. Next we could try some non-parametric tree based approaches that maybe able to better generalze our model.
-
Non-Parametric Models
-
DecisionTreeRegressor models usually tend to overfit due to their simplistic nature of spltting based on each feature based on entropy and gain or gini. However since this is a regression problem the split happens on the mean of the column and gini and entropy/gain is used only by DecisionTreeClassifier.
-
RandomForestRegressor seems to reduce overfitting which is greatly due to the randomness that this model brings into the picture and is based on the bagging framework. Essentially it takes a group of trees and a random set of data to train over. The randomness introduced helps to better generalize on the dataset. Random Forest uses the Bootstrapping or Pasting approach when selecting data for each tree. In bootstrapping data is selected with replacement where as in pasting there is no repetition of data for each tree learner. In most cases bootstrap = True does a much better job at both generalizing and increasing overall accuracy.
-
-
Adaboost (Adaptive Boosting)
- Adaboost introduces the concept of weights into decision trees and random forests and is moving towards deep learning approaches.
- Adaboost combines a lot of weak learners to make classifications.
- Some learners(tree stumps) get more say than others.
- Each stump is made by taking the previous stumps mistakes into account.
- At the start weights = (1/N (number of rows))
- Classification is checked for each feature and correct and incorrect classifications are obtained.
- Gini Index determines which stump will come first. Each stump is made of one feature. Lower gini index means feature will be the first stump.
- Total error = Sum of weights of correctly classified samples. (0-1). Lower is better.
- Amount of say (alpha):
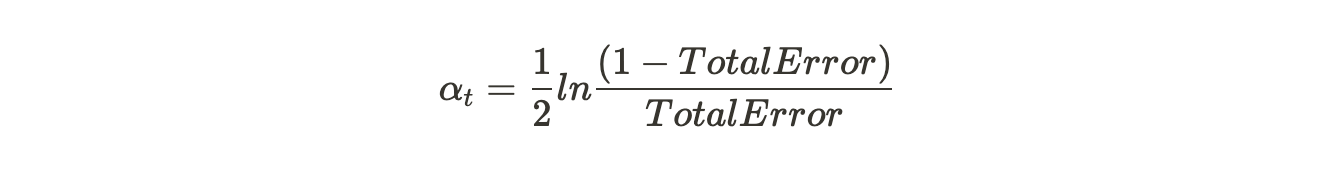
- In below diagram negative means it will reverse the classification output to make the incorrect classification correct. If error is 0.5, amount of say is 0.

-
The new sample weight = old sample weight * e^amount of say.
-
Next we will decrease the sample weights = sample weight * e^-amount of say. This is done to improve performance.
- After we have found the sample weight we will make this the new weights for the correct and incorrect classifications and normalize them. These weights will now be used for the next stump. To create a new collection of samples and get rid of the old samples.
- Adaboost seems to reduce overfitting when compared to decision trees and increases overall accuracy compared to RandomForest.
-
GradientBoostingRegressor: Next I decided to try gradient boosting regressor which was able to somewhat reduce the problem of overfitting however was not able to increase the accuracy score.
-
XGBoostRegressor: Lastly I have applied XGBoost regressor which reduced the overfitting problem by 2 basis points. XGBoost models are known to adjust both bias and variance and give the user a lot of control over how the data is being trained. The different parameters of xgboost and their significance:
- Max Depth: This parameter controls tree depth of all the weak learners. Having a lower depth would cause the model have a higher bias and reduce overfitting and introduce underfitting.
- SubSample: The SubSample is the amount of data that should be used to train for each tree. The data is different for each weak learner to better generalize. A higher value tends towards overfitting and a lower subsample tends towards underfitting.
- n_estimators: This is the number of weak learners that xgboost would use to make decisions. More number of estimators tends towards overfitting.
- learning_rate: The concept of gradient descent and deep learning comes to mind when learning rate comes into the picture. Just like in gradient descent where the algorithm is looking for global minima for loss, the same concept applies here as well. Too high a value and the loss swings to different points not attaining global minima and too low a value causes the model to take a longer time to train. Essentially we should adjust the learning rate in such a manner that we are able to get to global minima as well as not sacrifice too much on performance. Adjusting this parameter helps in regularization.
- colsample_bytree/level have the same effect on the model and help in regularization.
For all boosting models grid search cv was used for hyperparameter tuning and only a base model and a best parameters model were trained for comparison. Best parameters always gave us better results.
Deployment
- The front end of this app has been written by me using the bootstrap framework.
- I am using flask that allows me to deploy this app and conect the front end to the python code. Django is also an option here but I am not aware of how Django works however I would be looking at Django as well in the future and try to learn it as well.
- For deployment I decided to use Heroku for web deployment since it is free and the process of deployment is extremely simple.
Model Retraining Strategy
- Heroku allows for automatic deployment from our git repository. This means that I can configure a certain branch which in this case is my master branch to auto-deploy whenever any commits are made to this branch. This makes it extremely easy to retrain the model file that is saved at client side.
- Since I would be scrapping data every 3-4 days we would need to retrain the model every time data is collected. So I would run both jupyter notebooks manually every 3-4 days so that all files get updated and commit to git.
- Another approch I could try would be to use the windows task scheduler to do this for me. However I would not be pursuing any more changes to this project because it has already consumed a lot of my time.
Conclusion
-
I got hands-on experience in webscrapping, EDA, Feature Engineering, Feature Selection, ML model building, pandas, numpy, Bootstrap 4, Flask, git, stats, object oriented programming, versioning of files and keeping each version, geocoding location data, creating seperate html files and calling them from flask, pycharm, json, pickle and joblib for saving models,scikit-learn, xgboost, cross validation, grid search CV.
-
My intership of 4 months at Sunteck Realty gave me enough domain knowledge to handle certain features and have a strong grip over what I was doing since I was able to understand most of the real estate terminologies like carpet area, super area, loading, RERA etc. I also had descent knowledge on the prices of houses in area’s where Sunteck has their projects since all of us interns had shared this information about the projects with each other.
-
You can also check out this Project on github and also the Web app.
Thank You for reading.
